7 minutes - magazine 02 | 2025
Our journey to the smart factory ...
Networked, data-driven processes and intelligent systems are increasingly shaping the industrial world.
And at the heart of it is the smart factory, a highly automated production environment organized according to lean principles, combining modern automation technologies with digital tools. As the core element of Industry 4.0, it boosts companies’ competitiveness and ability to respond.

Johannes Mall, Head of Industrial Engineering
Modern robotics has a central role to play in this: cobots now take care of both monotonous and highly complex tasks and work hand in hand with humans. In assembly, logistics or quality assurance, they boost efficiency, improve safety in the workplace and increase the flexibility of production processes. AI-based applications are expanding these possibilities by analysing large volumes of data, recognising patterns, forecasting machine failure and optimising workflows. However, automation is always context-dependent, as Johannes Mall, Head of Industrial Engineering at Liebherr in Ehingen, knows: “Whereas standardised, highly automated processes are the norm in large-series production, for example at a car manufacturerʼs, the production processes for a construction equipment manufacturer involve smaller volumes and the wide variety of products requires more flexible systems.”
The smart factory is the future and we’re on board with it.
Classic mechanical engineering meets automation
“The smart factory is the future and we’re on board with it. Our strategy focuses on integrated modern robotics and AI technologies into our processes in order to improve efficiency and quality over the long term,” says Mall. While we’ve already made good progress in some areas towards a highly automated production environment, in other areas we’re still only just beginning. “We’re gradually developing innovative solutions ourselves and we’ll later be able to scale these to various areas,” explains Mall, adding: “Having this expertise in-house is good for future certainty and at the same time makes us independent.”
Production fit for the future – more than just process optimisation
Intelligent systems help to protect resources, lower energy consumption and reduce emissions. One example at the Ehingen site is the energy management system that continuously monitors and optimises key energy consumption. The integration of state-of-the-art building management technology and the use of renewable energies such as wind power and photovoltaics means that we have not only been able to reduce our CO₂ footprint, but we’ve also been able to significantly increase the energy efficiency of our production processes. By efficiently analysing data on heating and lighting control, as well as the use of compressed air, we’re able to make continuous improvements to achieve sustainable and resources-sparing production.
... Robotics, AI and automation in our production facilities
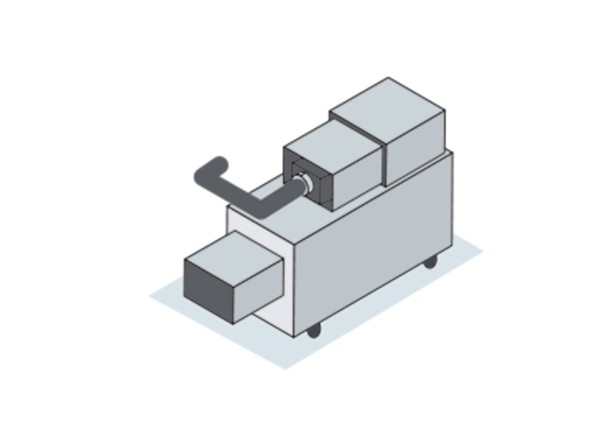
Hose production
AI and digitalisation
Hose production
In an automated process, hoses are cut with digital precision. The digital data comparison ensures high quality and guarantees the products’ fit and durability. Despite small batch sizes, production allows customer-specific adaptation. The digital processing of orders is cleverly integrated into the overall production process.
Quality management tool
For us, the QMT is a standard part of the production process: we have developed the software, including the testing station, in-house, enabling us to test the wiring of crane components and carry out a complete electrical function check. In LICCON3 drivers’ cabs, the system can test 320 pins fully automatically in ten minutes. In some cases, it can also test hydraulic components. Each check is documented for statistical analysis and used to continuously develop the QMT in order to adapt it to future component requirements.
Pick & place system
In hose and pipe assembly, an industrial robot takes care of the placement of union units and cutting rings. To do this, our engineers have developed an innovative solution that combines classic image processing with powerful AI technologies. Using camera snapshots, the parts are identified, the gripper coordinates are calculated and the perfect placement angle is determined.
Digital worker tools
The significant variations in our production processes means that they need to be reliable yet also flexible. One of the milestones in our journey towards the smart factory is therefore the digital preparation of information with deep integration of digital tools and electronic helpers for our employees.

Welding robots
Robotics
Welding robots
With a twin burner, our robots now weld two coordinated welding seams at the same time, achieving welding speeds of 120 cm / min. The finished seams reach minimum yield strengths of up to 1,100 N / mm². Thanks to offline programming, there are virtually no downtimes in production. Since the expertise of our highly qualified professionals goes hand in hand with technological progress, we are driving AI-assisted collaboration between humans and machines forward in this sector too.
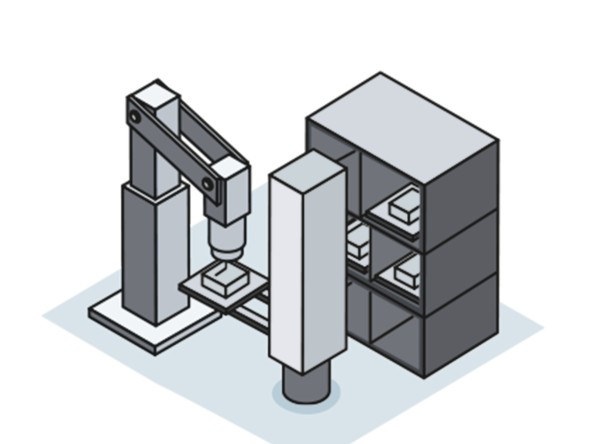
Automated milling centre and pallet handling system
Automation
Automated milling centre and pallet handling system
Material transporters bring raw and finished parts into the system on up to 240 Euro pallets at a time, taking them as required to set-up stations where they are prepared for milling in clamping equipment. Determined by a customer-specific algorithm, which calculates the system’s capacity, the parts clamped to the fixture pallets are forwarded to the pallet changer and then milled in one of the three processing centres. Outside shift times, the system processes clamped parts in an unmanned operation on up to 140 different fixture pallets. The entire system is characterised by the interplay of its high degree of automation and sophisticated logistics concept with a digital database.
Sheet metal processing
For the automated production of sheet metal parts, the punch laser machine automatically changes up to 90 tools from the Toolmaster. This allows complex jobs involving a lot of tool changes for various stages such as punching, bending, thread cutting or crimping to be carried out quickly and in an automated manner. Automatic loading and unloading is ensured by suckers that pick up sheets or blanks, bring them to the machine table and place the finished parts on unloading stations. The Grip- Master removes scrap skeletons and strips and stacks them on a scissor lift table – without any intervention from the operator.
Spare parts store
18,000 depots for palleted goods, six aisles, 40,000 small parts containers – in our automated warehouse, we manage the spare parts for our customers and branches. The large components are transported with a forklift truck, while the smaller ones are transported using modern conveyor technology. All of it is managed via a warehouse management system. This uses a material flow calculator which collects, analyses and communicates data relating to the best place to store material and how the picker can work their way through the system in the most efficient way.
Parts of logistics
Since April, the autonomous “PAOLO” forklift truck has been transporting goods on pallets and in pallet cages through the plant and supporting the logistics processes in mobile crane assembly. Whether it be axial discs, sheet metal or catalytic converters, the forklift brings them from the incoming goods area to the ‘supermarket’ as it’s known and returns empty pallets. Before it was commissioned, the human-machine interaction was tested extensively and optimised.
This article was published in the UpLoad magazine 02 | 2025.



